Entertainment Center Rebirth: Post-Flatscreen Solutions
The Evolution of Entertainment Centers: From CRT to Flatscreen
For decades, the entertainment center was defined by the bulky cathode-ray tube (CRT) television. These mammoth cabinets housed not just the TV but VCRs, gaming consoles, and shelves of media. The arrival of flatscreen technology—LED, LCD, and OLED—revolutionized home design. Suddenly, living rooms weren’t anchored by hulking furniture. Walls became focal points, and TVs morphed into sleek, frameless displays. But this shift left a void: what to do with the space once dominated by cabinetry? The answer lies in reimagining entertainment centers as multifunctional hubs that blend technology, aesthetics, and adaptability.
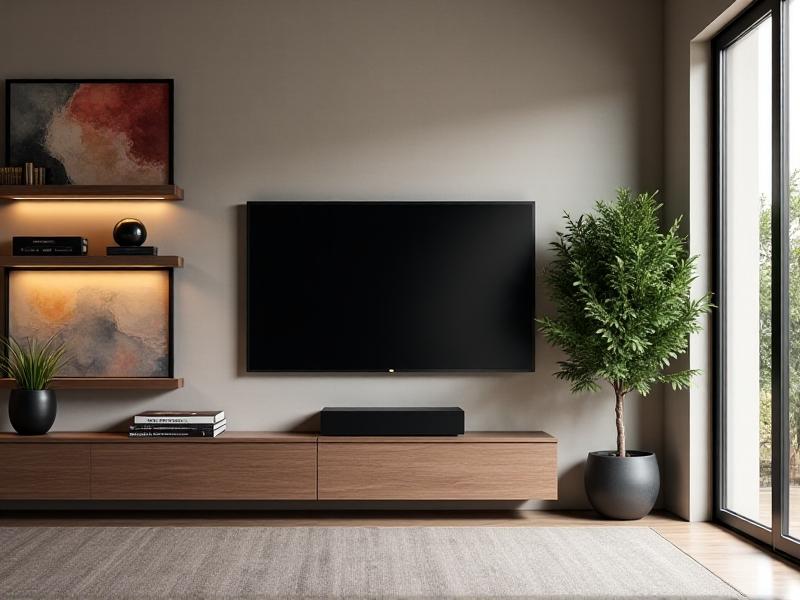

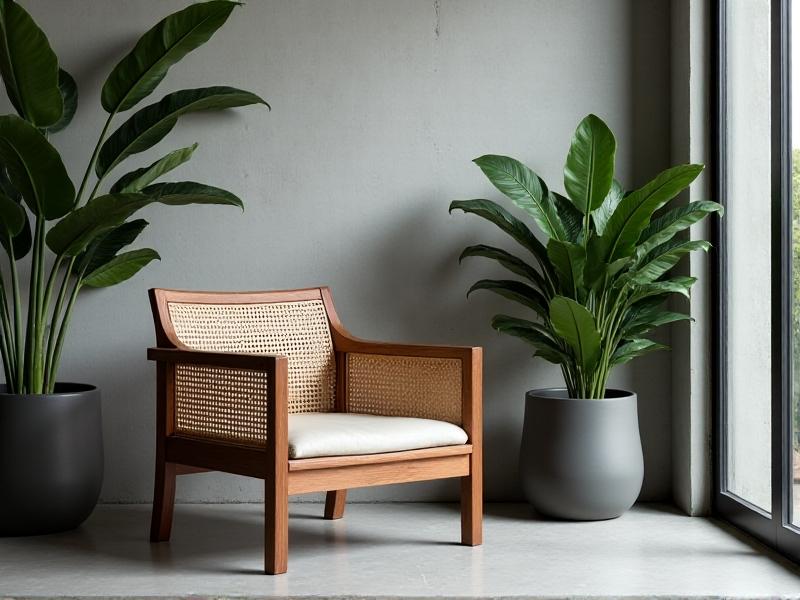
Minimalist Design: Embracing Negative Space
The post-flatscreen era prioritizes clean lines and uncluttered spaces. Floating consoles, concealed wiring, and hidden compartments replace bulky cabinets. Designers now emphasize “negative space,” using open shelving or wall-mounted units to create visual breathing room. Materials like brushed metal, tempered glass, and light-toned wood dominate, reflecting a shift toward airy, Scandinavian-inspired aesthetics. Storage solutions are discreet: pull-out drawers for gaming gear, magnetic panels for remote controls, and recessed niches for soundbars. The goal? To make technology invisible until it’s needed.

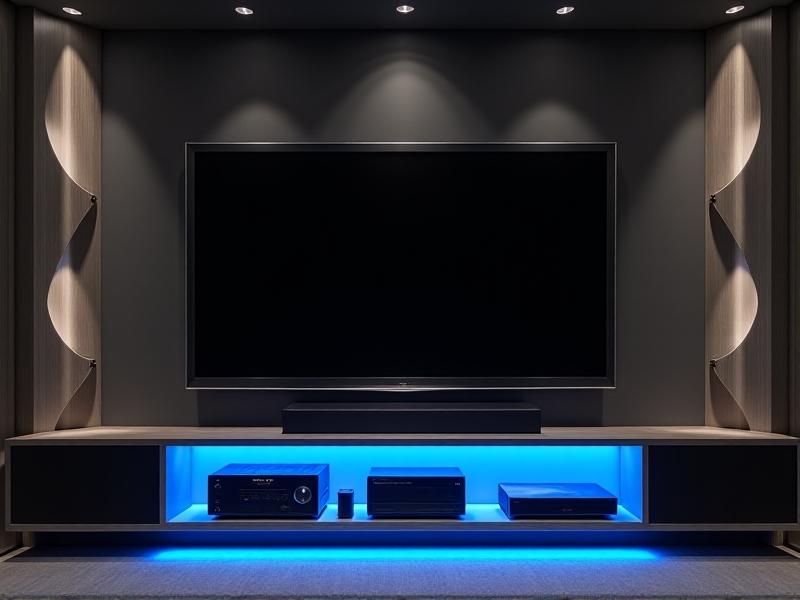
Immersive Audio: Soundscapes Over Speakers
As TVs slimmed down, audio quality suffered—until immersive sound technologies filled the gap. Dolby Atmos, soundbars with upward-firing drivers, and wireless surround systems now integrate seamlessly into modern setups. In-ceiling speakers disguised as recessed lighting or acoustic panels provide theater-grade sound without visual intrusion. Brands like Sonos and Bose offer modular systems that adapt to room layouts, proving that high-fidelity audio doesn’t require bulky subwoofers or tangled wires.

Smart Home Integration: The Invisible Command Center
Voice assistants and IoT devices have turned entertainment centers into smart home hubs. A single console might control lighting, climate, and security cameras via touchscreen interfaces or voice commands. Hidden compartments house Wi-Fi routers and NAS drives, while wireless charging pads built into tabletops keep devices powered. The result is a space where technology fades into the background, activated only by a spoken word or a tap on a smartphone.

Modular Furniture: Adapting to Tech’s Rapid Pace
With tech evolving faster than ever, static furniture feels obsolete. Enter modular systems: customizable units with interchangeable components. Think stackable cubes for game consoles, swappable faceplates to match new TV designs, and adjustable-height shelves for future gadgets. Companies like IKEA and BDI lead this trend, offering frames that let users reconfigure layouts as needs change—proof that flexibility is the new permanence.
Sustainability: Eco-Conscious Entertainment Spaces
The post-flatscreen movement aligns with eco-friendly design. Reclaimed wood media consoles, solar-powered charging stations, and energy-efficient LED backlighting reduce environmental impact. Brands prioritize recyclable materials and low-VOC finishes, while modular designs discourage disposable culture. Even packaging is part of the shift—flat-pack furniture minimizes carbon footprints, proving that cutting-edge tech and sustainability can coexist.